Discover the Foundations of Genetics
Explore the groundbreaking experiments of Gregor Mendel, the father of modern genetics. Understand the elegant laws of inheritance that revolutionized our understanding of life itself.


Gregor Mendel
Gregor Johann Mendel (1822-1884) was an Augustinian friar and scientist who conducted groundbreaking experiments on garden peas (Pisum sativum). Working in the monastery gardens of Brünn (now Brno, Czech Republic), Mendel systematically studied how traits are inherited from generation to generation.
Over eight years, between 1856 and 1863, Mendel cultivated approximately 28,000 pea plants, meticulously recording traits across seven characteristics. His mathematical approach and careful statistical analysis established him as the founder of scientific genetics, laying the cornerstone for modern heredity studies.
Mendel's Three Laws of Inheritance
Fundamental principles that govern how traits pass from parents to offspring
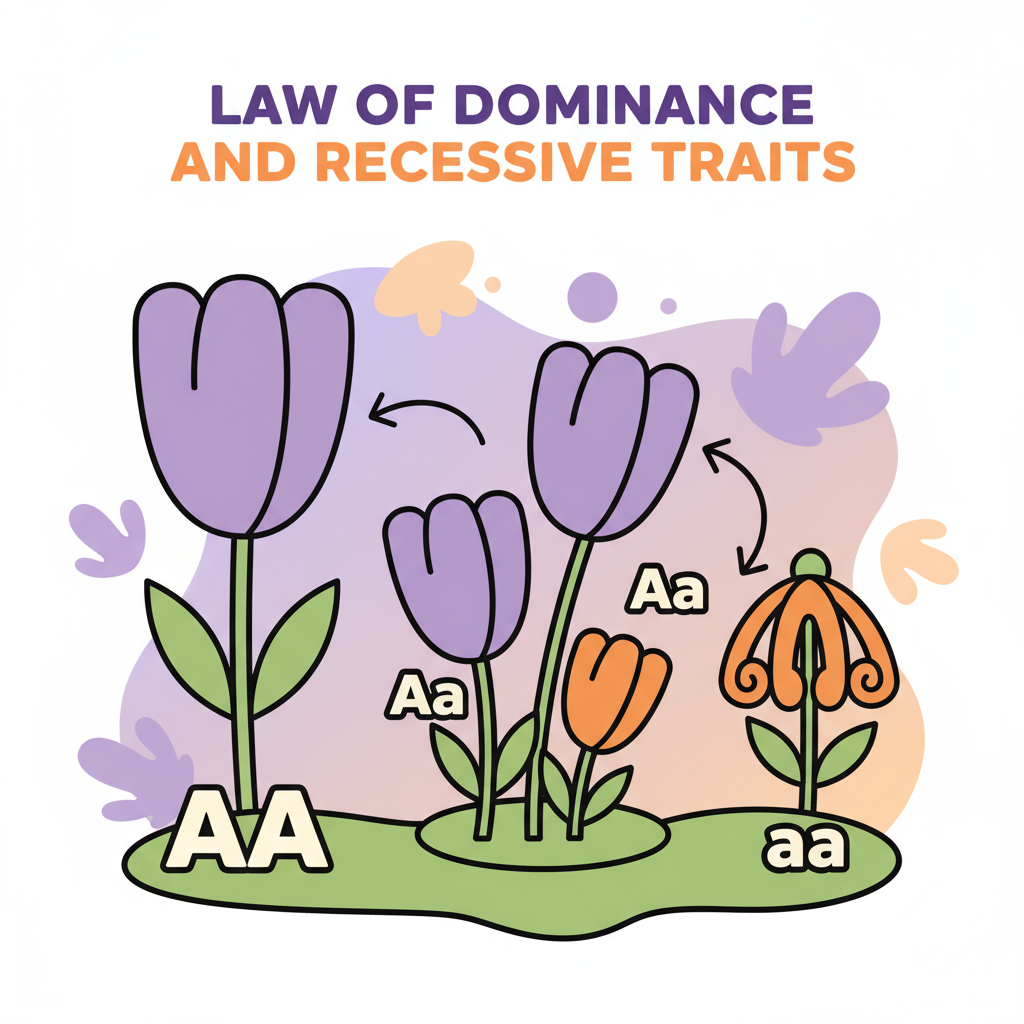
Law of Dominance
The First Law
When two pure-breeding parents with contrasting traits are crossed, the first generation (F1) offspring display only the dominant trait. The recessive trait is masked but not lost.
Example: Purple flowers × White flowers → All F1 plants have purple flowers (dominant)
F1 Ratio: 100% Dominant phenotype
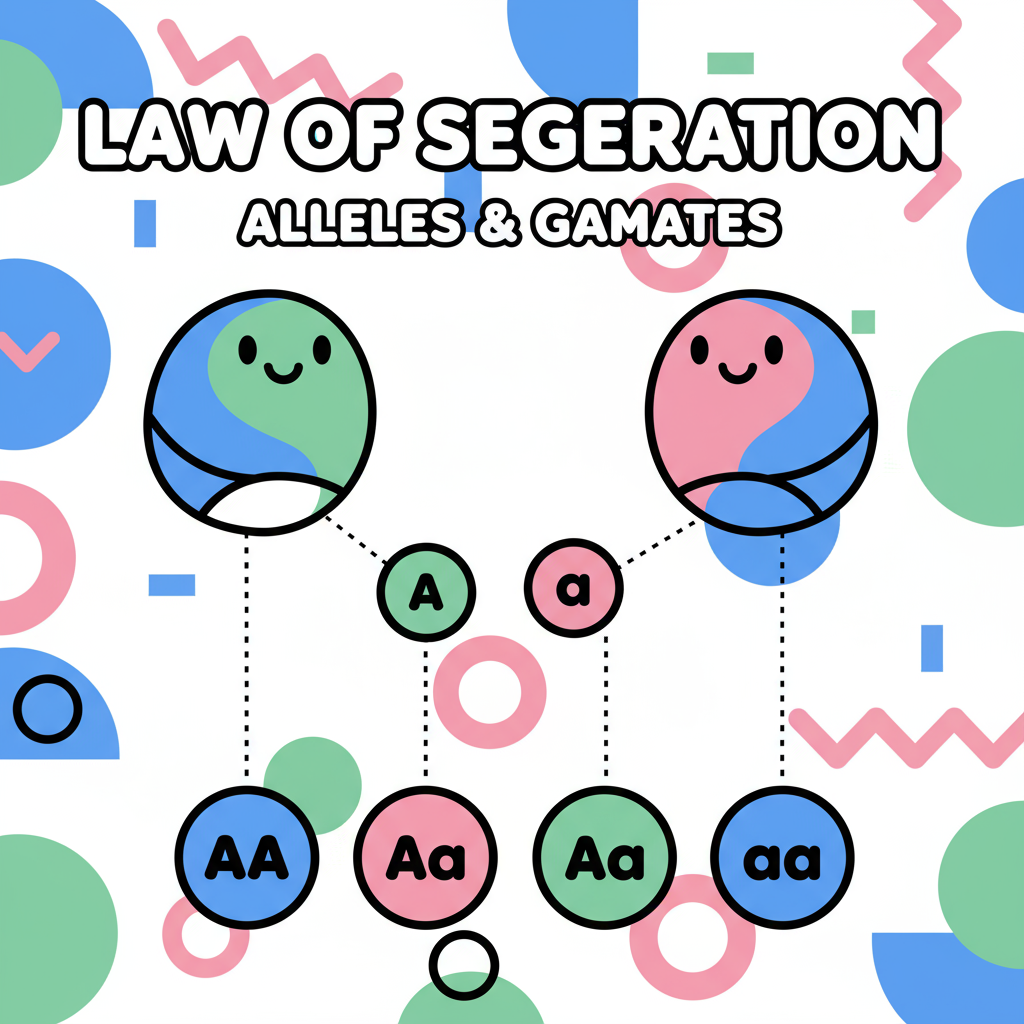
Law of Segregation
The Second Law
During gamete formation, allele pairs separate so each gamete receives only one allele. When F1 plants self-pollinate, both dominant and recessive traits reappear in F2 generation.
Example: F1 × F1 → F2 shows 3:1 ratio (3 dominant : 1 recessive)
F2 Ratio: 75% Dominant, 25% Recessive
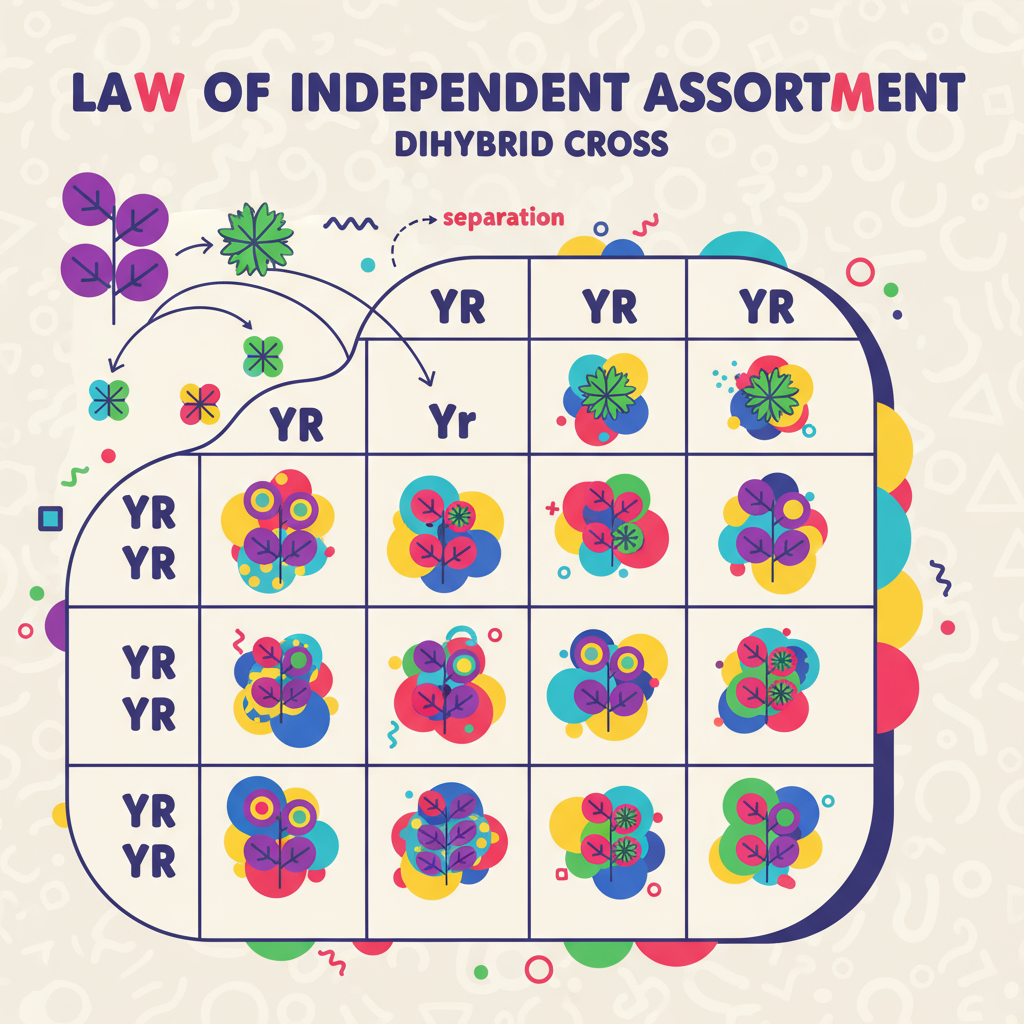
Law of Independent Assortment
The Third Law
Alleles of different traits segregate independently during gamete formation. Inheritance of one trait does not influence the inheritance of another trait.
Example: Seed color and seed shape are inherited independently, producing 9:3:3:1 ratio in F2
F2 Ratio: 9:3:3:1 (Dihybrid Cross)
Mendel's Systematic Experiments with Peas
Mendel didn't rely on chance or luck. He employed rigorous scientific methodology, studying seven contrasting traits across generations:
- Seed Shape: Smooth vs. Wrinkled seeds
- Seed Color: Yellow vs. Green seeds
- Pod Shape: Full vs. Narrow pods
- Pod Color: Yellow vs. Green pods
- Flower Color: Purple vs. White flowers
- Flower Position: Axial vs. Terminal blooms
- Plant Height: Tall (6-7 ft) vs. Dwarf (10-14 in) stems
Key Achievement: Mendel used statistical analysis with 28,000 plants, establishing the foundation for mathematical biology and proving his theories through empirical evidence.

Your Complete Learning Ecosystem
Mendel.in provides everything you need for NEET preparation with interactive content and comprehensive study materials
Theory Content
Comprehensive, expertly-written explanations covering genetics, heredity, and all biological concepts required for NEET entrance exams.
MCQ Tests
Thousands of carefully curated multiple-choice questions with detailed explanations, organized by topic and difficulty level.
Progress Tracking
Monitor your learning journey with detailed analytics, performance metrics, and personalized insights to identify areas for improvement.
Practice & Assessment
Regular quizzes and full-length practice papers that simulate real exam conditions to build confidence and exam readiness.
Smart Search
Quickly find specific topics, concepts, and questions with our intelligent search functionality across all study materials.
Dark & Light Modes
Comfortable studying at any time with adaptive interface modes designed to reduce eye strain during long study sessions.
Begin Your Genetics Journey Today
Join thousands of NEET aspirants mastering heredity, inheritance, and molecular biology through Mendel.in's comprehensive learning platform.
Access the Platform →